- Home
- About
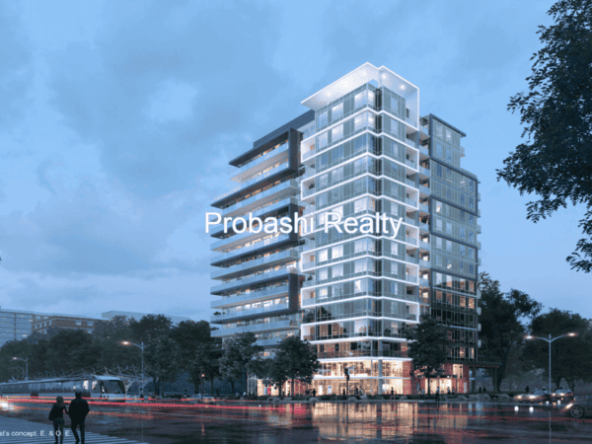
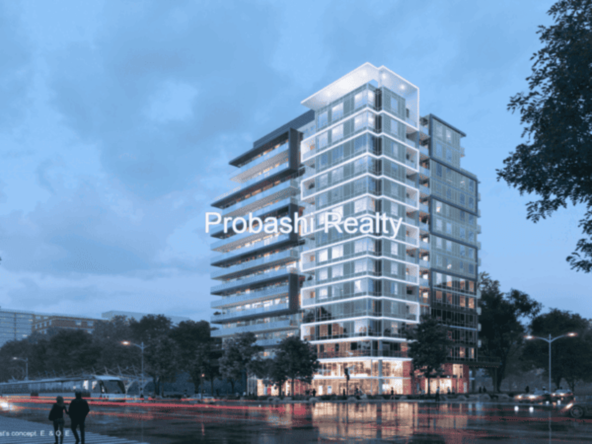
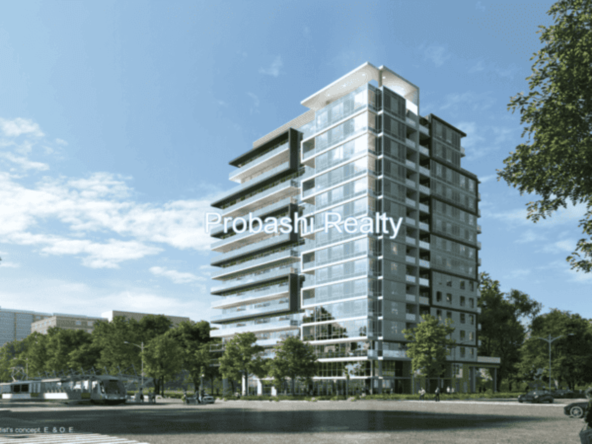
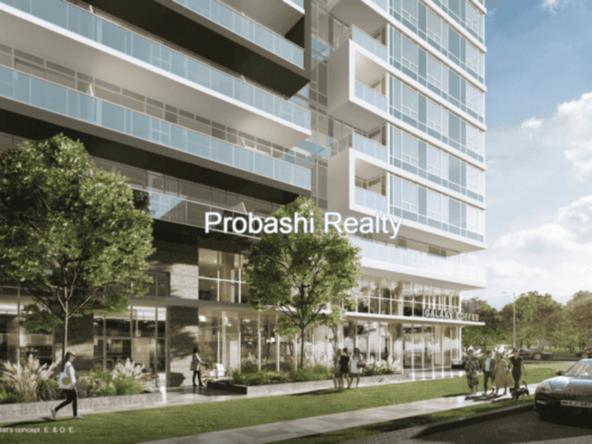
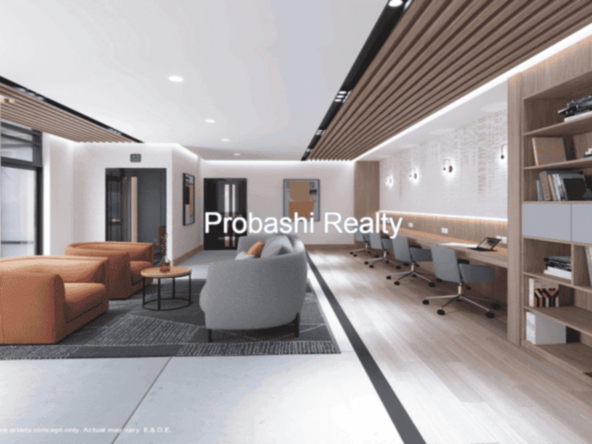
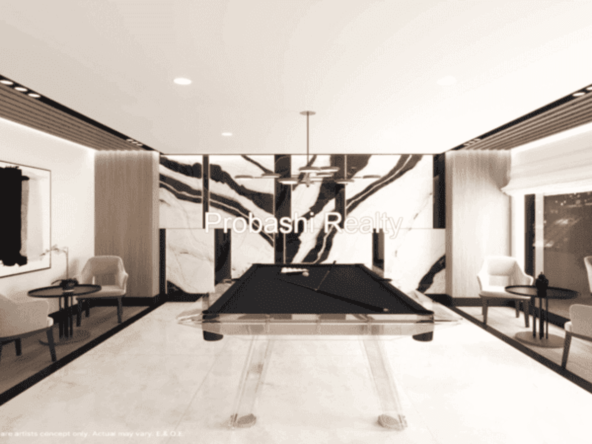
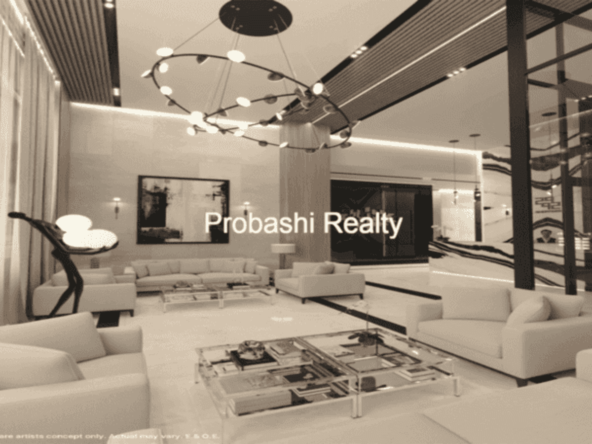
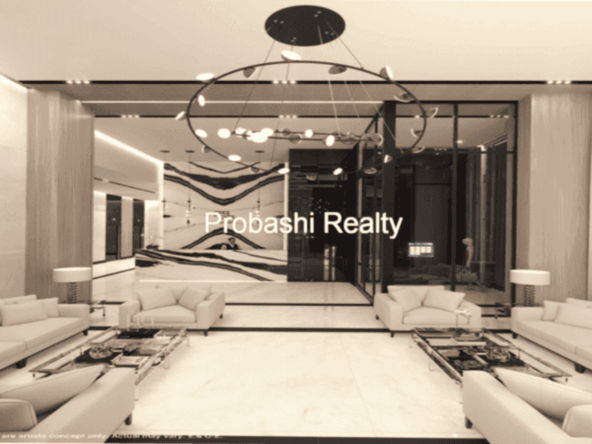
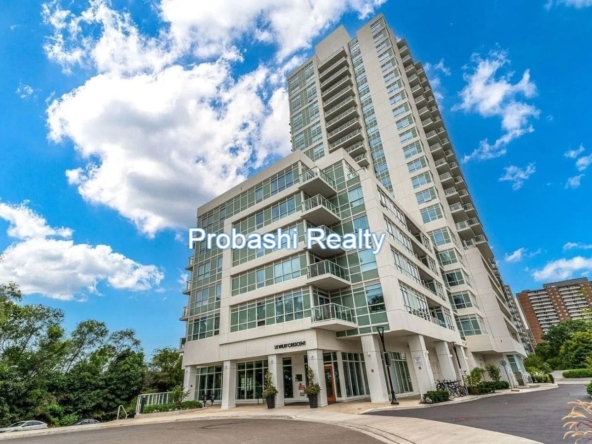
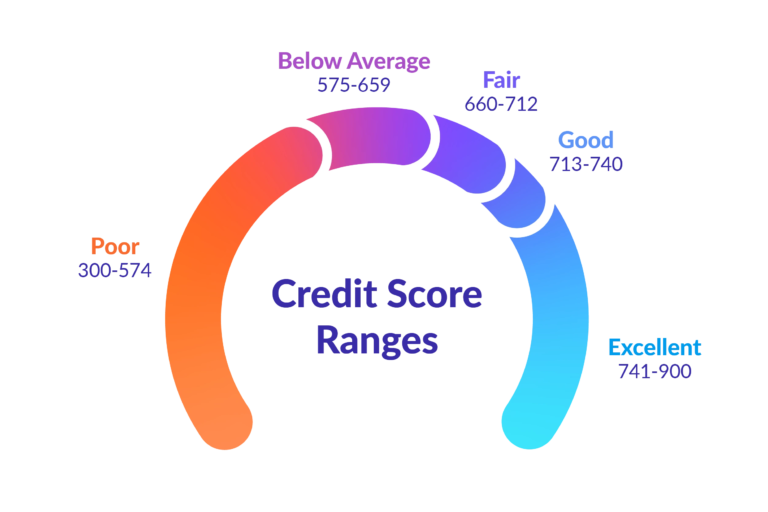
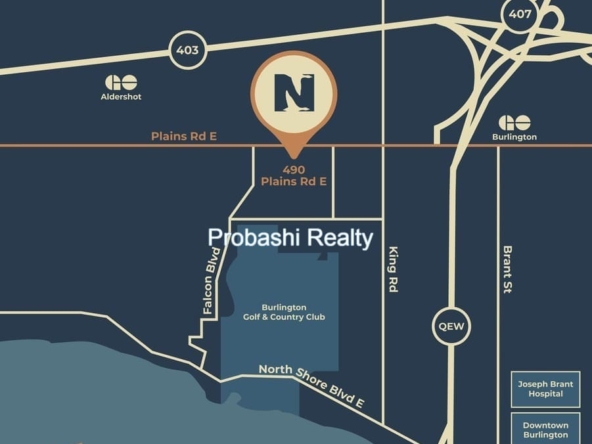
Probashi Realty is one of the world’s leading service companies specialized in the sale and rental of premium residential property and commercial real estate. Thanks to our unique and constantly expanding network and the strength of our brand, we have access to an exclusive clientele. We feel most at home among discerning individuals.Our company was created to revolutionize the real estate industry by improving the experience of buying and selling homes locally and internationally.

- Guide
Explore our guides for detailed insights into prime neighborhoods. Trust our expertise to help you find the perfect locale for your dream home, covering everything from local amenities to community vibes. We guide you through real estate intricacies, ensuring an informed and satisfying experience that aligns with your lifestyle. Your dream home awaits – let our guides lead the way.
- Blog
- Services
- Property Listing
- New Project
- Home Loan
- Foreign Bank
- Foreign Property
- Legal Services
- Partnership program
- Trends
- Interior
- Buy
- Sale
- Tools
- Add Property
- Contact Us
- Home
- About
Probashi Realty is one of the world’s leading service companies specialized in the sale and rental of premium residential property and commercial real estate. Thanks to our unique and constantly expanding network and the strength of our brand, we have access to an exclusive clientele. We feel most at home among discerning individuals.Our company was created to revolutionize the real estate industry by improving the experience of buying and selling homes locally and internationally.

- Guide
Explore our guides for detailed insights into prime neighborhoods. Trust our expertise to help you find the perfect locale for your dream home, covering everything from local amenities to community vibes. We guide you through real estate intricacies, ensuring an informed and satisfying experience that aligns with your lifestyle. Your dream home awaits – let our guides lead the way.
- Blog
- Services
- Property Listing
- New Project
- Home Loan
- Foreign Bank
- Foreign Property
- Legal Services
- Partnership program
- Trends
- Interior
- Buy
- Sale
- Tools
- Add Property
- Contact Us